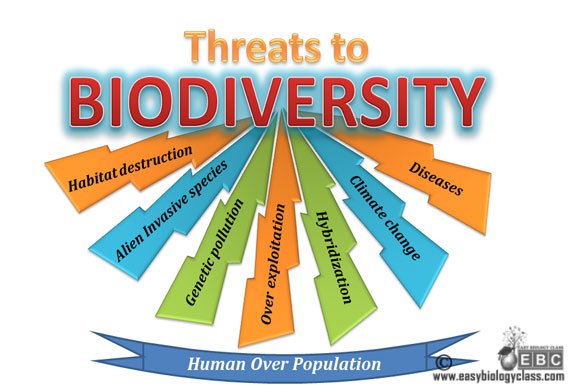
Biodiversity
Biodiversity
refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity typically
measures variation at the genetic, species, and ecosystem level. Terrestrial
biodiversity is usually greater near the equator, which is the result of the
warm climate and high primary productivity.
Biodiversity
Conservation
Conservation of biological
diversity is essential for the survival of the human race.
Objectives
and advantages of biodiversity conservation
·
Conservation of
biological diversity leads to conservation of essential ecological diversity to
preserve the continuity of food chains.
·
The genetic diversity of
plants and animals is preserved.
·
It ensures the
sustainable utilisation of life support systems on earth.
·
It provides a vast
knowledge of potential use to the scientific community.
·
A reservoir of wild
animals and plants is preserved, thus enabling them to be introduced, if need
be, in the surrounding areas.
·
Biological diversity
provides immediate benefits to the society such as recreation and tourism.
·
Biodiversity
conservation serves as an insurance policy for the future.
Biodiversity
conservation method
In-situ biodiversity
conservation
In-situ conservation
means the conservation of species within their natural habitats, this way of
conserving biodiversity is the most appropriate method for biodiversity
conservation. In this strategy you have to find out the area with high
biodiversity means the area in which number of plants and animals are present.
After that this high biodiversity area should be covered in the form of natural
park/ sanctuary/biosphere reserve etc. In this way biodiversity can be conserve
in their natural habitat from human activities
Ex-Situ conservation
methods
Ex-situ conservation
involves the conservation of biological diversity outside of their natural
habitats. This involves conservation of genetic resources, as well as wild and
cultivated or species, and draws on a diverse body of techniques and
facilities.
Ex-situ Biodiversity
conservation can be done as following:
• By forming Gene
banks: In this store seeds, sperm & ova at extremely low temperature and
humidity.
• It is very helpful
to save large variety of species of plants & animals in a very small space.
e.g. sperm and ova banks, seed banks.
• Forming Zoo and
botanical garden: for research purpose and to increase public awareness
collecting living organisms for aquaria, zoos and botanic gardens.
• Collections of In
vitro plant tissue and microbial culture.
• Captive breeding
of animals and artificial propagation of plants, with possible reintroduction
into the wild.



Very insightful
ReplyDeleteVery informative..
ReplyDeleteVery well written ..👍
ReplyDeleteQualitative information
ReplyDeletemethods for conservation of biodiversity are well explained.well written.
ReplyDeleteKeep blogging
Interesting and informative
ReplyDelete